Wrist Fractures
Wrist Fractures (distale Radiusfraktur)
Publications:
Lippisch et al distale Radiusfraktur Trauma und Berufskrankheit 2016
(Lippisch et al distale Radiusfraktur Trauma Occupational Diseases 2016)
Definition:
The distal radius fracture is colloquially referred to as "wrist fracture" and is the most common bone fracture in humans. With regard to the occurrence of this injury, two common types appear:
1. Young male patients, mostly in the context of work and sport accidents,
2. Older female patients, mostly by falls on the outstretched hand.
In older women, osteoporosis plays a special role as a risk factor, as even minor accidents can lead to bone fractures.
Symptoms:
After the fall on the hand shows a malposition of the wrist with pain, restriction of mobility and swelling. Furthermore, a bruise may occur and there may be tingling sensations in the hand.
Diagnostic und Therapy:
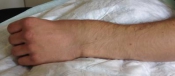 Often the inspection of the wrist already shows a suspected diagnosis. The accident mechanism must be clarified and after the physical examination, X-ray images of the wrist must be made in 2 levels.
Often the inspection of the wrist already shows a suspected diagnosis. The accident mechanism must be clarified and after the physical examination, X-ray images of the wrist must be made in 2 levels.
In the classification of the distal radius fractures, the position of the fracture as well as a possible involvement of the articular surface are considered. Furthermore, the accident mechanism allows a classification of the fractures: the fall on the outstretched hand leads to a so-called extension fracture (Colles fracture), while the fall on the bent hand leads to a flexion fracture (Smith fracture).
 The most common classification according to the Association for Osteosynthesis in fractures without involvement of the articular surface (A-fracture), fractures with partial joint involvement (B-fractures) and fractures with complete joint involvement (C-fracture). This results in indications for the therapeutic procedure.
The most common classification according to the Association for Osteosynthesis in fractures without involvement of the articular surface (A-fracture), fractures with partial joint involvement (B-fractures) and fractures with complete joint involvement (C-fracture). This results in indications for the therapeutic procedure.
After the X-ray has confirmed the suspicion of a wrist fracture, the fracture is readjusted. For this purpose, the hand is hung in the "girl catcher" and the arm is weighted with weights. Now the doctor can correct the joint position. Subsequently, a plaster splint is applied to the forearm.
For simple fractures without joint involvement (A-fractures) or fractures that can be adjusted very well, a therapy without surgery is possible. Here, the wrist can be immobilized in the plaster splint for 4-6 weeks so that the fracture heals.
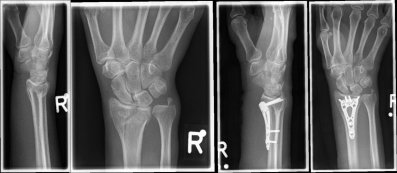
Pictures: A distal radius fracture with joint involvement (C-fracture) was treated with a plate osteosynthesis. After surgery, the plaster can be removed and physiotherapy exercises can be performed.
Complicated fractures involving the articular surface or dislocation should be surgically treated. Open fractures in which the skin is injured and bone is exposed require immediate surgical care. An involvement of the articular surface can lead to a restriction of the mobility in the wrist and therefore requires an anatomically exact reduction. The standard procedure for distal radius fractures is the provision of a titanium plate applied by the diffraction-side (palmar plate osteosynthesis) or the application of an external holder (external fixator).
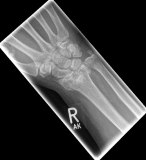
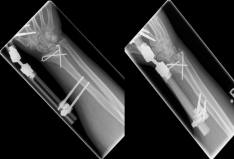
Pictures: In this case, the articular surface of the wrist was completely destroyed, so that only a therapy by means of outer retainer and some K-wires to correct the position was possible. Here is a practice only after removal of the outer holder after 6-8 weeks possible. Such severe joint injuries often lead to premature joint wear
After Treatment:
For the conservative treatment of a wrist fracture, the forearm gypsum can be removed after 6 weeks. Thereafter, intensive physical and occupational therapy exercise is very important. Only then can mobility and strength be regained after the long period of immobilization of the wrist.
If a wrist fracture is surgically treated with a titanium plate, wrist exercises may begin on the first day after surgery. Due to the early functional exercise, a long immobilization of the forearm and thus muscle loss is avoided. Thus, the previous range of motion can be achieved faster. Even after discharge from the hospital, daily exercise is the most important means of achieving rapid healing progress.






